We dissect the June 2025 Iran–Israel–US flare-up, map possible military and diplomatic trajectories, and quantify cascading shocks to energy, shipping, agriculture, tech, and automotive supply chains. Through rich case studies India’s rice trade, European chip fabs, African crude imports we reveal acute and chronic vulnerabilities. We then present a strategic playbook covering stakeholder incentives, sanctions spillovers, innovative risk finance, and KPI-driven dashboards to help firms pre-empt and adapt to enduring volatility.
Introduction & Context
- Timeline Recap: • June 13: Israel begins sustained strikes on Natanz and missile depots. June 21–22: U.S. launches Maverick‐armed raids on Fordow and Isfahan. June 23 onward: Iranian proxies in Lebanon and Yemen target shipping lanes; daily market jitters ensue.
- Historical Backdrop: • 2015 JCPOA suspended sanctions in exchange for enrichment caps; U.S. “snap-back” threat loomed if Iran cheated. 2020 Soleimani strike prompted limited Iranian missile response, illustrating Tehran’s calibrated restraint. Red Sea harassment by Houthis since 2019 offers a preview of supply‐chain shockwaves.
- Market Reactions: • Brent up 12% in one week; U.S. bond yields dip as safe-haven capital flows surge. Container freight index spikes 30% on Suez rerouting; war-risk surcharges double for Gulf calls.
Current Dynamics & Escalation Pathways
Iran’s Arsenal of Options
- Ballistic Missile Salvos: Follow-on launches at U.S. bases in Iraq, akin to the January 2020 IRGC operation, capped to avoid full U.S. counterstrikes.
- Mine Warfare & Fast Boats: Deploy sea mines and explosive‐drone boats in Hormuz mirroring 1987 “Tanker War” tactics to force tanker convoys at 5-kn slow‐steaming pace.
- Cyber & EW Attacks: Disrupt Israeli desalination plants and U.S. military datalinks via known APT28-style intrusions, demonstrating strategic reach sans kinetic escalation.
U.S./Israeli Escalation Ladders
- GBU-72 Deep Strikes: Target Iran’s hardened launch centers beneath 80 meters of rock denying IRGC free bunker use.
- Proxy Leveraging: Israel opens a third front by striking Hezbollah’s HQ in Beirut suburb; U.S. arms and trains anti-IRGC Kurdish cells near Erbil.
- “Off-Ramp” Diplomacy: Washington floats phased, verifiable uranium roll-backs, conditioned on Gazprom-style on-site inspections.
Regional Spillovers
- Lebanon: Heavy exchanges at the Blue Line force UNIFIL reinforcement; Lebanese ports stymie Lebanese-Syria trade.
- Red Sea: Houthi attacks surge to 10 vessels/week; Maersk, MSC divert 50% of Suez‐bound loads around Cape Town, adding 10 days/voyage.
- Gulf Monarchies: UAE reconsiders hosting U.S. fifth-generation jets; KSA escalates Patriot deployments around Ras Tanura and Jeddah.
Supply Chain Implications: Sectoral Deep Dive
Energy Markets & Infrastructure
- Oil Price Trajectories: • Short spike: +40% Brent on Hormuz mine reports. Mid-term plateau: +15% above $85 for 6–12 months if maritime risk persists.
- Natural Gas: Straits disruptions push Qatar to offer LNG spot cargoes at a $3/MMBtu premium to Asia; European buyers accelerate LNG FSRU leases.
Maritime Chokepoints & Logistics
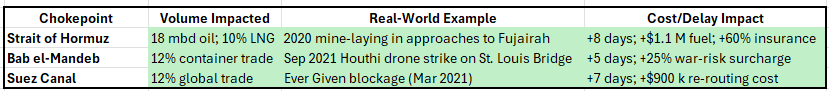
Sector Case Studies
- Agriculture (India & Egypt): Iran halts rice imports; India reroutes 200 k tons to Iraq at lower margins. Egypt’s wheat shipments delay 7 days via Cape to Alexandria, fueling domestic bread crises.
- Semiconductors (Taiwan, Germany): TSMC and Infineon shift tool shipments to Zeebrugge via northern Europe; 5 days extra in transit yields 12% lower fab utilization.
- Automotive (Europe & Japan): VW’s Zwickau plant sources billet from Bahrain and Switzerland to substitute lost Abu Dhabi steel, adding +$150/ton and delaying model launch by two quarters.
- Pharmaceuticals: Insulin intermediate shipments from E. Med ports delayed; Novo Nordisk taps buffer stocks in Singapore to avoid shortages in EU.
Resilience & Mitigation Strategies
- Network Redundancy: Dual-sourcing of Iranian petrochemicals from Gulf and Latin America; leverage Brazil’s ethanol for chemical feedstock blends.
- Strategic Stockpiles: Create 60-day safety stocks of critical items (IC substrates, pharma intermediates) at regional hubs in Rotterdam, Singapore, and Jebel Ali.
- Adaptive Logistics: Partner with intermodal rail operators across Central Asia (Trans-Caspian) to form “shadow routes” with dynamic capacity allocation.
- Financial Derivatives: • Oil options collars to cap price spikes at $90 pb. FX forwards for AED/USD to lock in transshipment costs.
- Real-Time Command Center: Integrate maritime AIS feeds, sanctions-sanctioned entity databases, and predictive-analytics engines into a unified war-room for 24/7 rerouting decisions.
Long-Term Predictions & Regional Supply Chain Effects
- Chronic Premiums: A $7–12 pb structural uplift in Brent for 18-24 months; Asian refiners pay up to $8/MMBtu over JKM LNG spot.
- Reroute Entropy: 20% of Europe-Asia container volume permanently via Cape and Northern Sea Route (seasonal).
- Energy Transition Surge: Middle East solar-to-hydrogen megaprojects Neom’s OXAGON and UAE’s Al Maktoum FSRU hub accelerate by 30% in planned capacity.
- GCC Strategic Pivot: KSA signs new 10 mtpa LNG deals with Japan and South Korea; Iran anchors Turkmenistan gas via Qazvin-Turkey pipeline.
- Manufacturing On/near-shoring: Samsung expands Austin fab; Germany’s Infineon opens 12-inch plant in Saxony to cut Middle East transit exposure.
Lessons from Other Geopolitical Conflicts
- Gulf War (1990–91): Kuwait/Saudi pipeline‐break closures forced tanker diversions around Cape – cost +$2.5 M per VLCC.
- Iran–Iraq War “Tanker War”: Both navies mined Hormuz; tankers paid war-risk up to 1.5% of value, insurers set deductibles at $10 M before payout.
- Crimea Annexation (2014): EU sanctions on Russian banks led Gazprom to pre-pay Chinese buyers in RMB, deepening Sino-Russian financial linkages.
- Red Sea Attacks (2019–21): Maersk’s “Orange 1” reroutes cost $150 M extra annually; spurred naval coalitions and convoy protocols.
- COVID-19 Supply Shock: Apple’s iPhone delays from Foxconn led to multi-month product massaging; Honda paused European assembly lines for critical sensor shortages.
Additional Analytical Dimensions to Include
- Cyber & Hybrid Warfare Risks: Impact on port-terminal OT networks, ICS/SCADA vulnerabilities, digital forensics.
- ESG & Humanitarian Corridors: Environmental liabilities from mine pollution; red-cross logistics planning.
- Geospatial Intelligence: Satellite imagery analytics for ship-tracking, minefield detection, refugee-flow mapping.
- Crisis Governance: Organizational war-room protocols, C-suite escalation ladders, cross-functional crisis exercises.
- Cultural & Social Dynamics: Workforce readiness, cross-border staff evacuation plans, local labor union exposure.
Stakeholder & Political Economy Mapping
State Actors
- United States Incentives: Prevent nuclear breakout, reassure Gulf allies, protect global oil flow. Levers: Carrier strike groups, sanctions, strategic dialogues with Kuwait, Qatar, Oman. Negotiation Channels: Direct ENSAs with Tehran via Oman intermediaries; American-Saudi security pacts.
- Israel Incentives: Eradicate Iranian nuclear threat, weaken Hezbollah, safeguard home-front morale. Levers: Air Force sortie rates, secret tech transfers (bunker-buster munitions), Mossad back channels. Channels: U.S. National Security Council, covert Russian de-confliction in Syria.
- Iran Incentives: Preserve regime, advance nuclear capability, deter Israeli attacks. Levers: IRGC ballistic/missile arsenal, proxy networks, Hormuz blockade threat. Channels: Supreme Leader’s envoys to Iraq and Oman, Chinese/Russian diplomatic cover at UNSC.
Non-State Actors
- Hezbollah Incentives: Protect Iranian lifeline, assert Lebanese political clout. Network: Cross-border tunnels, Iranian drone technology, local recruitment.
- Houthis Incentives: Pressure Saudi coalition, extract Yemeni concessions. Network: Iranian Quds Force logistical pipelines via Oman.
- Kurdish Militias (Iraq/Syria) Incentives: Weakening IRGC footprint, leverage for autonomy talks. Channels: U.S. Special Operations liaisons, Peshmerga training programs.
Commercial Actors
- Shipping Lines: Maersk & MSC: Re-designing ultra-large containership loops to avoid Gulf. Front-line terminals (Fujairah, Salalah): Lobbying for naval convoy support.
- Energy Majors: Shell & Total Energies: Splitting crude procurement between GCC and West Africa; using SPR releases for price smoothing.
- Insurers & Underwriters: Lloyd’s of London: Issuing parametric war-risk products; syndicating Middle East risk among global pools.
Interdependencies & Negotiation Channels
- U.S.–GCC Security Dialogue: Five-year renewals of base-sharing agreements tied to Gulf states’ anti-missile defense purchases.
- EU Mediation: E3 back-channel talks in Vienna, using Iranian oil revenues held in South Korean escrow as bargaining chips.
- China/Russia: Arms-for-energy multipliers Beijing’s $400 b pipeline financing to Tehran; Moscow’s S-300 deployments in Syria as de-escalation signals.
Conclusion
The U.S. joining Israel’s kinetic campaign escalates the Middle East into a multi-domain crisis. Iran’s mix of missile, maritime, cyber, and proxy tactics though calibrated threatens sustained disruptions. Corporates must leapfrog from reactive reroutes to proactive resilience: multi-modal networks, financial hedges, digital twins, and stakeholder alignment will define who weathers this era of chronic geopolitical risk.
